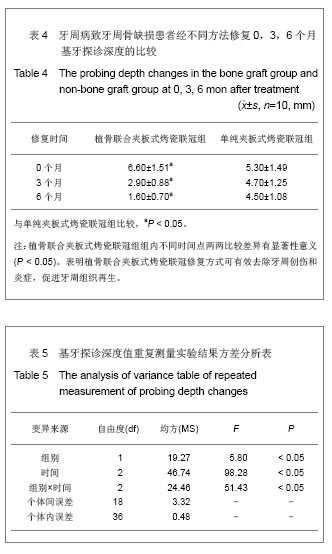
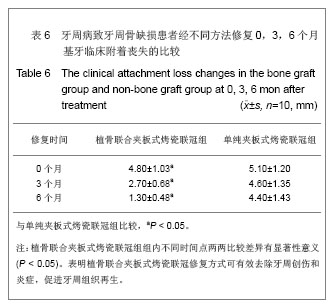
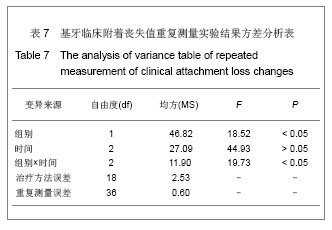
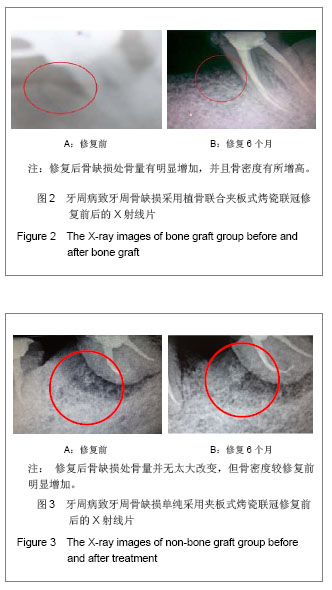
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (34): 6103-6109.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.34.007
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
烤瓷夹板联合植骨修复牙周骨缺损基牙牙周的变化
李 征1,崔 杰1,王 星1,满云娜2,李 亮3,何惠宇1
- 新疆医科大学第一附属医院,1口腔修复科,3临床医学研究院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;2乌鲁木齐市口腔医院牙周科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000
Periodontal bone graft in combination with splint-like porcelain-fused-metal bridge for repair of periodontally compromised abutment
Li Zheng1, Cui Jie1, Wang Xing1, Man Yun-na2, Li Liang3, He Hui-yu1
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, the First Affiliated Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Periodontics, Stomatological Hospital of Urumqi, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Institute of Clinical Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
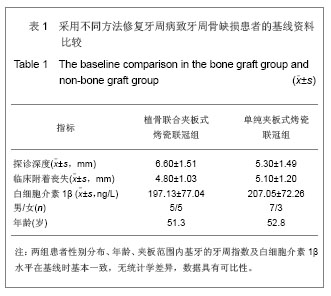
背景:采用夹板式固定义齿修复牙周炎致牙周骨缺损伴牙列缺损可增加根周骨质骨密度,但并未增加骨高度,因此,仅运用单纯的夹板式固定修复牙周炎致牙周骨缺损伴牙列缺损具有一定的局限性。
目的:对比牙周植骨联合夹板式烤瓷联冠与单纯夹板式烤瓷联冠修复牙周病致牙周骨缺损患者基牙的牙周变化。
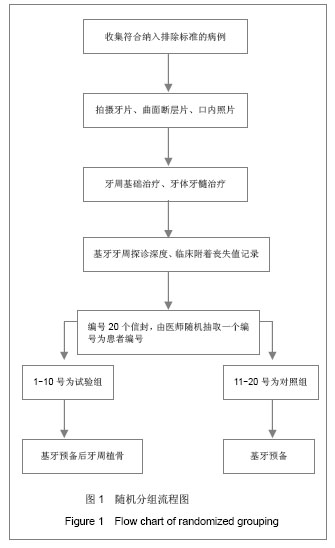
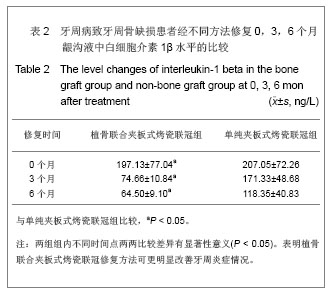
方法:选择牙周炎伴Kennedy Ⅲ类牙列缺损、远中牙牙槽骨角形吸收拟行烤瓷冠修复患者20例,抽签随机分为试验组与对照组,每组10例。试验组采用牙周植骨联合夹板式烤瓷联冠修复,对照组采用单纯夹板式烤瓷联冠修复,夹板戴入后0,3,6个月采集两组待测基牙龈沟液,检测龈沟液中白细胞介素1β水平,并复查和记录探诊深度与临床附着丧失。
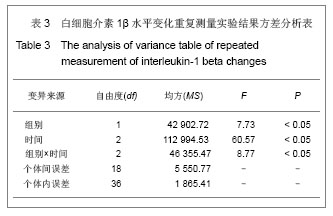
结果与结论:两组龈沟液中白细胞介素1β水平均随着时间推移逐渐下降(P < 0.05),且不同时间点试验组下降程度高于对照组(P < 0.05)。两组基牙探诊深度、临床附着丧失均随着时间推移逐渐下降,不同时间点试验组较对照组下降更明显(P < 0.05),且试验组组内不同时间点各指标差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。结果表明牙周植骨联合夹板式烤瓷联冠较单纯夹板式烤瓷联冠修复方法更利于维持和促进牙周骨缺损患者基牙的健康,并可获得较满意的近期临床疗效。
中图分类号: